
In a recent peer-reviewed publication, Dr. Renee Dufault, an American scientist affiliated with the Food Ingredient and Health Research Institute, has introduced a validated research protocol to examine how ultra-processed foods influence prenatal heavy metal exposure and expression of the zinc-dependent metallothionein-1 (MT-1) gene—critical factors affecting child neurodevelopment.
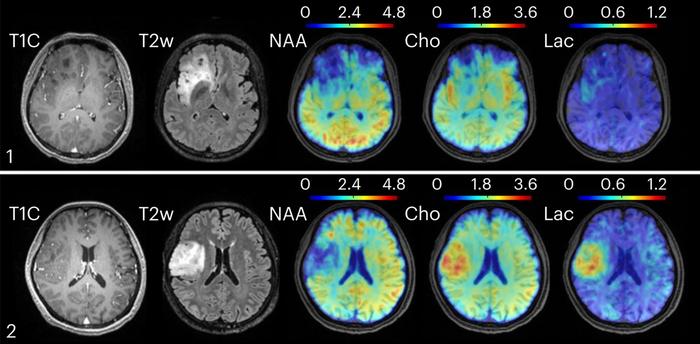
CHAMPAIGN, Illinois, July 2025 — A pioneering advance in brain imaging technology developed at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign promises to revolutionize our understanding of brain function and disease. Scientists have introduced a novel magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) method that enables high-resolution metabolic imaging of the whole brain in just over 12 minutes—using standard clinical MRI machines.
Read more: Fast Metabolic MRI Offers New Insights into Neurological Disorders

25 Years of the Human Genome Project: Unlocking Life’s Code and Imagining the Next Frontier
Twenty-five years ago, an extraordinary milestone was reached in science and medicine: the first full draft of the human genome was completed. The announcement marked the culmination of a decade-long international effort involving over a thousand scientists across six countries, decoding nearly all three billion letters of our DNA—the master code of life.
Back then, the promises were as bold as they were ambitious: a revolution in diagnosing, preventing, and curing diseases like Alzheimer’s, cancer, and diabetes by targeting their genetic roots. While some hopes were premature, the reality has been a story of steady, remarkable progress—and an even more exhilarating future.
A sweeping change is underway in the diagnosis and treatment of traumatic brain injury (TBI), as experts worldwide introduce the CBI-M framework—a multidimensional system designed to provide a far more detailed and individualized understanding of each patient’s condition.
Read more: New Multidimensional Framework Set to Revolutionize Brain Injury Diagnosis

In a remarkable leap forward for neuro-oncology, scientists in the UK have unveiled a pioneering diagnostic tool that dramatically cuts the waiting time for brain tumour classification — from the current six to eight weeks down to just two hours. This new test, called ROBIN (Rapid Nanopore Brain Intraoperative Classification), promises to transform both surgical decision-making and patient care.
Read more: Ultra-Fast Brain Tumour Test Revolutionises Diagnosis



{noindex} Amsterdam, April 29, 2025 — A new study published in The Lancet Regional Health – Europe reveals that researchers at Amsterdam UMC have developed a fast, affordable diagnostic test to detect bacterial meningitis with high accuracy using C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Read more: Breakthrough CRP Test Accelerates Diagnosis of Bacterial Meningitis
Page 2 of 4