A recent experimental study published in LabMed Discovery has found that a nanoemulsion formulation of vitamin D3 significantly improves core symptoms of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in young children. The research offers a new direction in nutritional interventions for neurodevelopmental disorders.
Children with ASD frequently present with low serum vitamin D3 levels, which have been linked to impairments in language development, adaptive behavior, and motor coordination. While traditional vitamin D3 supplements have yielded inconsistent results, this study evaluated whether a nanoemulsion—engineered to improve bioavailability—could provide more consistent clinical benefits.
The randomized controlled trial enrolled 80 children aged 3 to 6 years with diagnosed ASD. Participants were divided into two groups: one received a nanoemulsion-based vitamin D3 formulation, and the other received a standard commercial vitamin D3 product. Both groups underwent supplementation for six months.
Outcomes were assessed using standardized tools, including the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS), the Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scale, and the Preschool Language Scale. The nanoemulsion group demonstrated statistically significant improvements in:
- Vitamin D3 serum levels
- Severity of autism symptoms
- Social IQ
- Receptive and expressive language skills
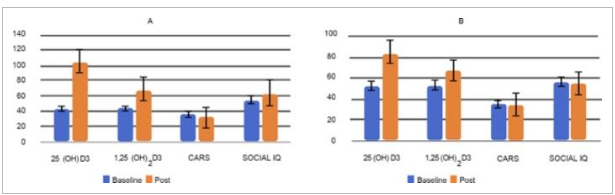 Comparisons of baseline levels and the post-supplementation levels in group I (A) and II (B) A: P values for the change of the 2 types of vitamin D3 (P < 0.000,1), CARS scores (P = 0.000,2), and social IQ (P = 0.04) in group I; B: P value for the 2 types of vitamin D3 (P < 0.000,1; P = 0.02), CARS scores (P = 0.4), and social IQ (P = 0.8) in group II (CARS: childhood autism rating scale; IQ: intelligence quotient)
Comparisons of baseline levels and the post-supplementation levels in group I (A) and II (B) A: P values for the change of the 2 types of vitamin D3 (P < 0.000,1), CARS scores (P = 0.000,2), and social IQ (P = 0.04) in group I; B: P value for the 2 types of vitamin D3 (P < 0.000,1; P = 0.02), CARS scores (P = 0.4), and social IQ (P = 0.8) in group II (CARS: childhood autism rating scale; IQ: intelligence quotient)
In contrast, the group receiving the conventional supplement showed improved serum vitamin D3 levels but no meaningful behavioral or cognitive improvements.
The study concludes that the nanoemulsion formulation offers superior clinical benefits by enhancing the absorption and effectiveness of vitamin D3. The authors recommend further research with larger cohorts and long-term follow-up to confirm these findings and to explore potential gender-specific responses.
This research highlights the potential of nanotechnology-based delivery systems to transform the landscape of therapeutic nutrition in pediatric neurodevelopmental care.
Published: May 16, 2025
Journal: LabMed Discovery
DOI: 10.1016/j.lmd.2025.100071