Benign familial neonatal epilepsy is a rare autosomal dominant epileptic syndrome characterised by frequent brief seizures within the first days of life.
Clinical features
-
Seizures mainly occur in full-term normal neonates following a normal pregnancy and delivery and without precipitating factors. Seizures are brief, of 1–2 min and may be as frequent as 20–30 per day.
-
The tonic phase is followed by a clonic component which is usually asymmetrical and unilateral
-
The post-ictal state is brief
-
The neonate is asymptomatic interictally
-
Pure clonic or focal seizures are rarely seen[4]
Electroencephalography
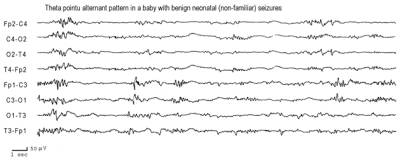 theta pointu alternant (source: Plouin et al(1992)[5]
theta pointu alternant (source: Plouin et al(1992)[5]
-
The inter-ictal EEG may be normal, discontinuous, have focal or multifocal abnormalities or have a theta pointu alternant pattern
-
The apnoea and tonic motor activity corresponds to synchronous and bilateral flattening of 5–19s on the ictal EEG
-
followed by bilateral and often asymmetrical discharges of spikes and sharp waves with a duration of 1–2 min, coinciding with the vocalisations, chewing and focal or generalised clonic activity.76,77
Genetics
-
inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern and shows a high degree (approximately 85%) of penetrance
-
A few cases result from new mutations in the KCNQ2 on chromosome 20q 13.3 or KCNQ3 on chromosome 8q.13.3. 11 mutations have been identified in KCNQ2 while two have been identified in KCNQ3 all leading to the same phenotype.
-
Berkovic et al have reported that mutations in the sodium channel subunit gene SCN2A are specific to ‘benign familial neonatal-infantile seizures’
Pathophysiology
-
Loss of function of heteromeric voltage-gated potassium channels that reduce the potassium current impairs repolarisation of the neuronal cell membrane results in hyperexcitability of the brain resulting in seizures.
-
Okada et al(2002)[6] have suggested that BFNC cannot be produced by KCNQ-channel dysfunction alone but by reciprocal action between impaired KCNQ channel and other conditions which results in either an increase in excitation or decrease in inhibition.
-
Potassium channels shown differential expression at different stages of maturation which might be another explanation for the pathogenesis of BFNS[7]
Differential diagnosis
-
Benign neonatal seizures (non-familial)
| Benign (non-familial) neonatal seizures | Benign familial neonatal seizures | |
|---|---|---|
| Main seizures | Mostly clonic | Tonic-clonic |
| Onset | Fifth day of life | Second or third day of life |
| Duration of seizures | Status epilepticus (median 20 hours) | Repetitive isolated seizures |
| Main causes | Unknown, probably environmental | Autosomal dominant |
| Subsequent seizures | Practically nil (0.5%) | Relatively high (11%) |
| Psychomotor deficits | Minor | Practically non-existent |
| Ictal EEG | Usually localised spikes | Usually generalised flattening |
| Interictal EEG | Usually theta pointu alternant | Normal or focal abnormalities |
| Source: The Epilepsies: Seizures, Syndromes and Management. Panayiotopoulos CP. Oxfordshire (UK): Bladon Medical Publishing; 2005. | ||
-
Benign familial infantile epilepsy
Prognosis
-
Seizures remit between 1 and 6 months from onset, majority during the first 6 weeks[4].
-
10–14% may later develop other types of febrile (5%) or afebrile seizures including idiopathic generalised seizures. Rolandic seizures have also been reported.
-
Although an exception deaths during neonatal seizures have also been reported
-
the prevalence of learning disabilities is reported to be around 2.5% which is not significantly different to that in the general population[10]
Management
-
seizures usually remit spontaneously without medication
-
The use of anti-seizure medications does not influence the eventual outcome
-
if the seizures are prolonged benzodiazepines or phenytoin may be used to terminate them
-
counselling parents about this familial condition with generally good prognosis is important
References
1. . Electroclinical signs of benign neonatal familial convulsions. Ann Neurol. 1993 Dec;34(6):835-41. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340613.
[PMID: 8250533] [DOI: 10.1002/ana.410340613]
[PMID: 8250533] [DOI: 10.1002/ana.410340613]
2. . Seizure characteristics in chromosome 20 benign familial neonatal convulsions. Neurology. 1993 Jul;43(7):1355-60. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.7.1355.
[PMID: 8327138] [DOI: 10.1212/wnl.43.7.1355]
[PMID: 8327138] [DOI: 10.1212/wnl.43.7.1355]
3. . Benign familial neonatal convulsions: evidence for clinical and genetic heterogeneity. Ann Neurol. 1991 May;29(5):469-73. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290504.
[PMID: 1859177] [DOI: 10.1002/ana.410290504]
[PMID: 1859177] [DOI: 10.1002/ana.410290504]
4. Panayiotopoulos CP. (2005). The Epilepsies: Seizures, Syndromes and Management. Oxfordshire (UK): Bladon Medical Publishing.
5. . Benign familial neonatal-infantile seizures. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Dec;16(4):595-9. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160417.
[PMID: 6660252] [DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160417]
[PMID: 6660252] [DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160417]
6. . Impaired M-current and neuronal excitability. Epilepsia. 2002;43 Suppl 9:36-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1528-1157.43.s.9.9.x.
[PMID: 12383278] [DOI: 10.1046/j.1528-1157.43.s.9.9.x]
[PMID: 12383278] [DOI: 10.1046/j.1528-1157.43.s.9.9.x]
7. Vidaurre JA, Ballaban-Gil KR, Plouin P, Moshe SL. Benign neonatal familial seizures. In: Gilman S, editor. Medlink Neurology. San Diego SA: Arbor Publishing Corp; 2004
8. . Benign familial neonatal seizures: clinical and electroencephalographic characteristics. Pediatr Neurol. 1986 Sep-Oct;2(5):272-5. doi: 10.1016/0887-8994(86)90018-4.
[PMID: 3508699] [DOI: 10.1016/0887-8994(86)90018-4]
[PMID: 3508699] [DOI: 10.1016/0887-8994(86)90018-4]
9. . Benign familial neonatal seizures. Arch Neurol. 1980 Jan;37(1):47-8. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500500077012.
[PMID: 7350900] [DOI: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500500077012]
[PMID: 7350900] [DOI: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500500077012]
10. . Familial neonatal and infantile seizures: an autosomal-dominant disorder. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jul;18(3):455-9. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180315.
[PMID: 6476007] [DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180315]
[PMID: 6476007] [DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180315]

